Google is taking a decisive step toward a more anticipatory form of artificial intelligence. A new beta feature for Gemini, first reported by TechCrunch, enables the AI assistant to provide proactive responses based on a user’s photos, emails, messages, and other personal data sources. Rather than waiting for explicit prompts, Gemini can now surface suggestions, reminders, and insights automatically—bringing Google closer to its long-standing vision of a truly intelligent digital assistant
This update represents a meaningful shift in how users interact with AI. Instead of asking questions, users may increasingly receive relevant information before they even realize they need it. While the feature remains in beta, its implications for productivity, privacy, and the future of AI assistants are significant.
For years, AI assistants have operated primarily in a reactive mode. Users issue commands, ask questions, or request summaries. Gemini’s new proactive capability suggests a transition from “assistant” to something closer to a digital partner, capable of understanding context and acting independently within defined boundaries.
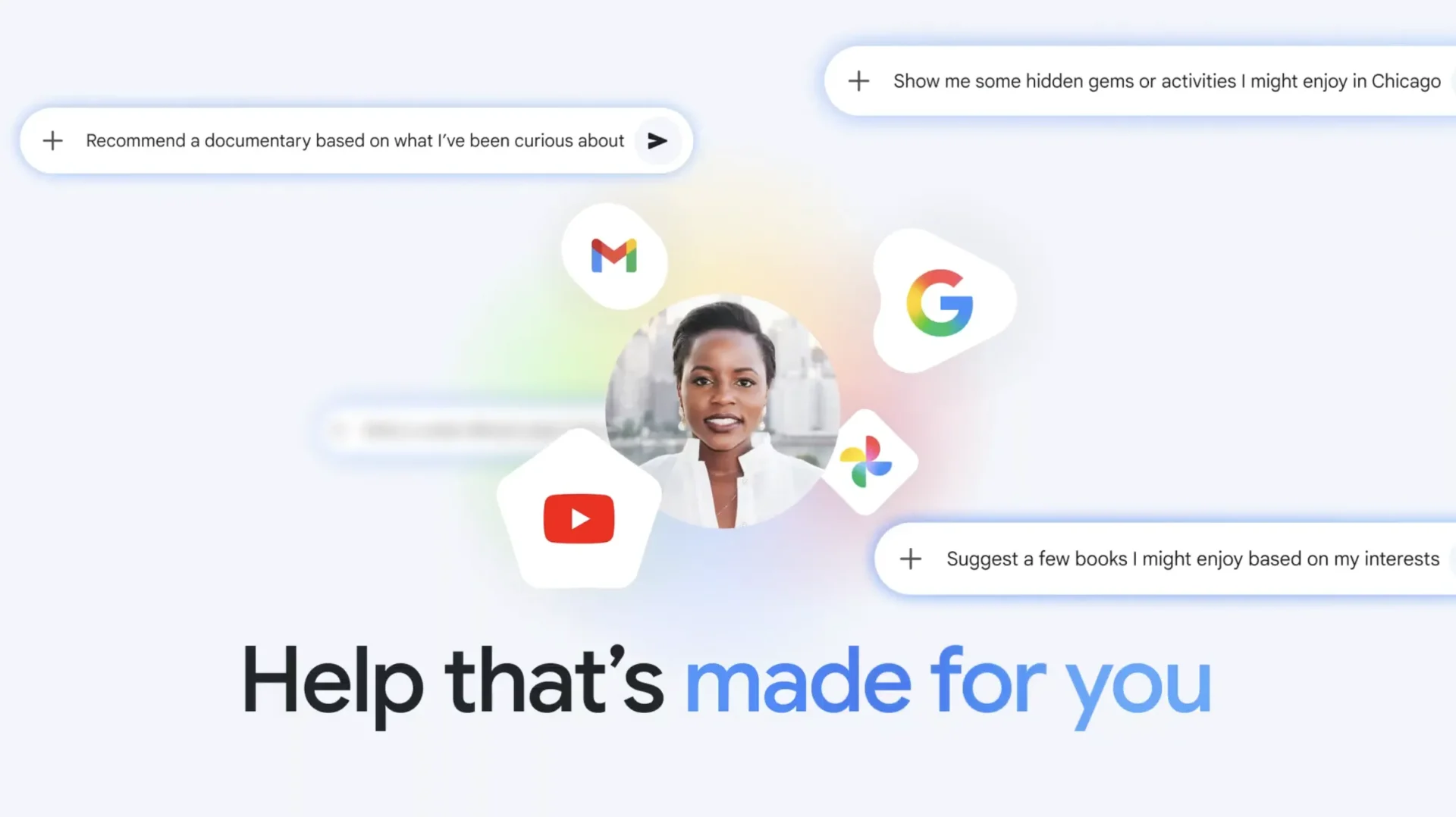
Google’s approach leverages its unique advantage: deep integration across services such as Gmail, Photos, Calendar, and Drive. By connecting these data sources, Gemini can form a richer understanding of a user’s daily life and provide timely, relevant guidance.
At the core of the new beta feature is Gemini’s ability to analyze multimodal inputs. This includes text-based content like emails and documents, as well as visual data from photos. By combining these inputs, Gemini can infer intent, detect patterns, and anticipate needs.
For example, if a user receives an email about an upcoming event and has related photos or documents stored elsewhere, Gemini may proactively suggest reminders, packing lists, or follow-up actions. This type of contextual awareness moves beyond simple keyword matching and into deeper reasoning.
Google’s emphasis on proactive responses reflects broader trends in AI development. As large language models grow more capable, the challenge shifts from generating text to delivering value at the right moment. Gemini’s beta feature aims to solve that problem by embedding intelligence into everyday workflows.
Rather than replacing existing tools, Gemini acts as a connective layer. It draws insights from multiple services and presents them in a unified, conversational format. This approach aligns with Google’s long-term goal of reducing friction across its ecosystem.
One of the most notable aspects of the update is how it reframes productivity. Traditional productivity tools require users to actively manage tasks, deadlines, and information. Gemini’s proactive responses suggest a future where the system takes on more responsibility for organization and planning.
This could fundamentally change how people interact with digital information. Instead of searching through inboxes or photo libraries, users may rely on Gemini to surface what matters most at the right time.
However, this increased intelligence also raises important questions about privacy and trust. Proactive AI requires access to personal data, and users must feel confident that this data is handled responsibly.
Google has emphasized that the Gemini beta includes user controls and transparency around data usage. Users can choose which data sources Gemini can access and can disable proactive features if desired. These safeguards will be critical in determining whether users embrace or resist this new form of AI assistance.
The beta nature of the feature suggests that Google is proceeding cautiously. Proactive AI is powerful, but it also carries risk. Incorrect or poorly timed suggestions could frustrate users or erode trust. By testing the feature with a limited audience, Google can refine accuracy, relevance, and tone.
Early beta feedback will likely shape how aggressively Google rolls out proactive capabilities in the future. Subtlety will be key. An assistant that interrupts too often or offers obvious suggestions may feel intrusive rather than helpful
Gemini’s evolution also highlights intensifying competition in the AI assistant space. Major technology companies are racing to define the next generation of personal AI. Proactivity is emerging as a key battleground.
What sets Google apart is its unparalleled access to contextual data. While other AI systems excel at conversation or creativity, Google’s ecosystem integration gives Gemini a unique vantage point. This update demonstrates how Google plans to capitalize on that advantage.
From a technical perspective, proactive AI places heavy demands on reasoning and relevance filtering. Gemini must determine not only what information is available, but what is useful in a given moment. This requires sophisticated models capable of prioritization and judgment.
The beta feature suggests that Google is confident in Gemini’s ability to handle these challenges at scale. It also signals progress in multimodal AI, where understanding images and text together unlocks new possibilities.
The potential use cases extend well beyond productivity. Proactive responses could enhance travel planning, event coordination, personal archiving, and even wellness tracking. By analyzing photos and messages, Gemini could surface memories, detect routines, or highlight anomalies worth attention.
This breadth of application makes Gemini less like a single-purpose tool and more like a foundational layer for digital life management
Still, adoption will depend heavily on user comfort. Proactive AI blurs the line between assistance and autonomy. Users must trust that Gemini’s actions align with their goals and values.
Google’s challenge will be to balance initiative with restraint. The most successful proactive features are likely to be those that feel intuitive and supportive rather than disruptive.
The beta release also reflects Google’s broader AI strategy. Rather than launching flashy standalone products, Google is embedding AI deeply into existing services. This incremental integration allows users to experience benefits without changing habits dramatically.
Gemini’s proactive responses are a natural extension of this philosophy. They enhance familiar tools rather than replacing them.
Industry observers see this move as a step toward the long-promised vision of ambient computing. In this model, technology fades into the background, offering assistance seamlessly and contextually.
Gemini’s beta feature is not yet fully ambient, but it points clearly in that direction. The assistant becomes aware of what users are doing and what they might need next.
There are also implications for how people manage information overload. As data volumes grow, the ability to filter and prioritize becomes increasingly valuable. Proactive AI could act as a personal curator, highlighting what matters and suppressing noise.
If executed well, this could reduce cognitive load and improve focus. If executed poorly, it could add another layer of distraction.
The response from early users will be critical. TechCrunch’s reporting suggests cautious optimism, with interest tempered by questions about control and accuracy. These reactions mirror broader public sentiment around AI: excitement mixed with concern.
Google’s transparency and responsiveness during the beta phase will likely determine whether proactive Gemini features become widely adopted.
In the context of AI history, Gemini’s update marks a shift from tools that respond to commands to systems that anticipate needs. This evolution has long been discussed in theory, but practical implementations have been limited.
By leveraging its ecosystem and advances in AI reasoning, Google is now testing that theory in the real world
The long-term success of proactive AI will depend on personalization. Gemini must learn individual preferences, communication styles, and tolerance for intervention. One-size-fits-all proactivity is unlikely to succeed.
Google’s ability to personalize at scale will be a defining factor in Gemini’s future.
As AI assistants become more proactive, ethical considerations will also grow. Questions about consent, data boundaries, and algorithmic bias will become more prominent. Google will need to engage with regulators, researchers, and users to navigate these challenges responsibly.
The beta phase provides an opportunity to identify and address issues before broader deployment.
Ultimately, Gemini’s new feature represents a meaningful step forward in AI usability. It shifts the focus from impressive demos to everyday value. Rather than asking what AI can do, the question becomes how AI can quietly make life easier.
This is a subtle but profound change in framing.
Conclusion: Gemini Moves From Reactive Assistant to Proactive Partner
Gemini’s new beta feature signals a turning point in the evolution of AI assistants. By delivering proactive responses based on photos, emails, and personal context, Google is redefining what it means to be “helpful.”
While challenges around privacy, accuracy, and user trust remain, the potential benefits are substantial. If refined carefully, proactive Gemini could reduce friction, improve organization, and bring AI closer to its promise of seamless support.


![[CITYPNG.COM]White Google Play PlayStore Logo – 1500×1500](https://startupnews.fyi/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/CITYPNG.COMWhite-Google-Play-PlayStore-Logo-1500x1500-1-630x630.png)