SpaceX has successfully launched the Starlink 6-100 mission, adding more satellites to its growing low Earth orbit broadband constellation. The launch underscores SpaceX’s aggressive deployment strategy and the intensifying global race for satellite-based internet access.
SpaceX continues to press its advantage in the satellite internet market. According to Space.com, the company launched its Starlink 6-100 mission from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, deploying another batch of broadband satellites into low Earth orbit and reinforcing the scale of its global connectivity ambitions.
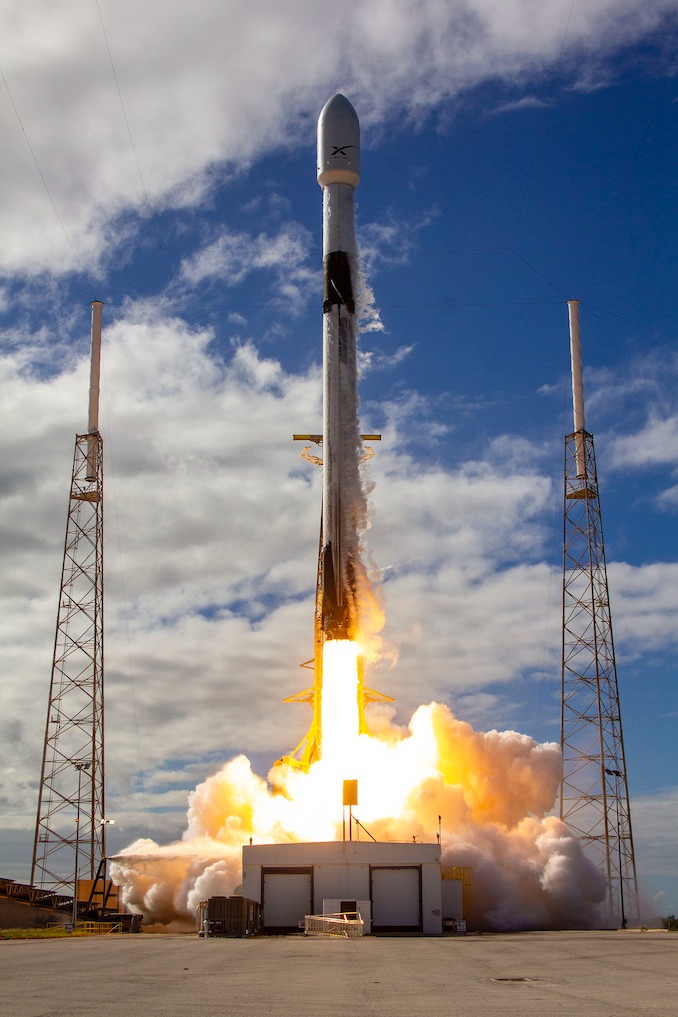
The mission flew aboard a Falcon 9 rocket, using booster B1080, which successfully completed its flight and landing sequence. While individual Starlink launches have become routine, their cumulative impact is anything but. Each mission brings SpaceX closer to a fully global, high-capacity satellite network—one that is already reshaping how internet access is delivered in remote, rural, and underserved regions.
For the broader space and startup ecosystem, the launch illustrates how operational cadence, not just technological novelty, has become SpaceX’s defining advantage.
What the Starlink 6-100 mission adds
SpaceX’s Starlink 6-100 mission deployed a new set of satellites designed to enhance network capacity and coverage. SpaceX has not publicly detailed whether this batch includes its latest-generation satellites with expanded throughput, though recent missions have increasingly featured upgraded hardware.
The Falcon 9 booster used for the mission landed successfully after launch, continuing SpaceX’s strategy of rapid reuse to drive down costs and maintain high launch frequency. This operational model allows SpaceX to deploy satellites at a pace unmatched by most competitors.
While SpaceX regularly publishes launch confirmations, it does not always disclose granular performance data immediately, leaving some technical specifics to emerge over time.
Why Starlink’s scale matters
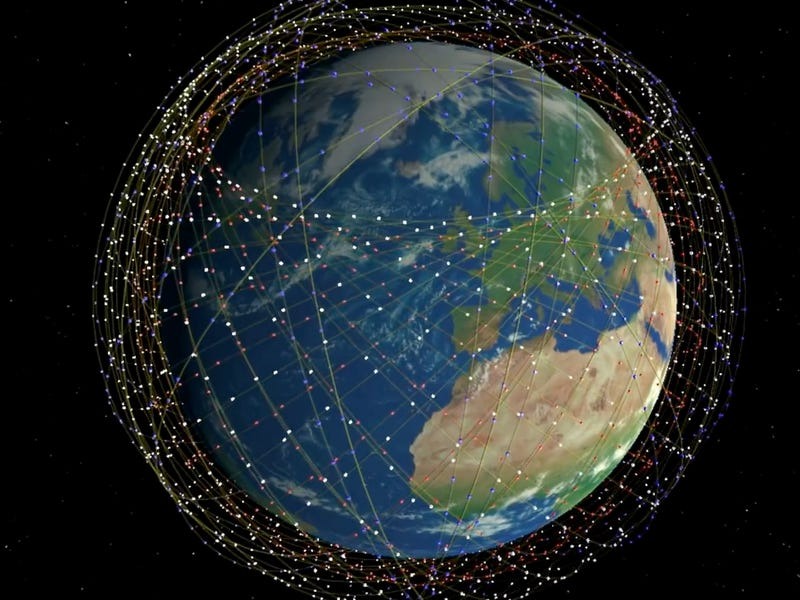
Starlink is no longer an experimental project. With thousands of satellites already in orbit, the constellation represents one of the largest privately operated space infrastructures ever built.
The business case is increasingly clear: terrestrial broadband networks struggle to reach remote or geographically challenging areas, while satellite internet can offer coverage almost anywhere on Earth. Starlink has found early traction among rural users, maritime operators, aviation customers, and governments seeking resilient communications.
Each additional launch strengthens SpaceX’s ability to offer higher speeds, lower latency, and more reliable service—key factors as competition in satellite broadband intensifies.
Competitive pressure across the space industry
SpaceX’s rapid deployment schedule is setting a high bar for rivals. Other satellite internet providers face a difficult challenge: matching Starlink’s scale without SpaceX’s vertically integrated launch capability.
This dynamic is reshaping investment flows in the space sector. Startups and established players alike are increasingly focused on niche applications, specialized orbits, or complementary services rather than attempting to replicate Starlink’s mass-market approach.
At the same time, regulators worldwide are paying closer attention to orbital congestion, spectrum allocation, and long-term sustainability as mega-constellations become the norm rather than the exception.

Implications for startups and global connectivity
For startups, Starlink’s expansion cuts both ways. On one hand, ubiquitous satellite broadband lowers barriers for building global services, enabling connectivity-dependent products in regions previously considered unreachable.
On the other, SpaceX’s dominance raises questions about platform dependency. Companies building on top of satellite connectivity must consider pricing power, service continuity, and regulatory variability across markets.
Nevertheless, the overall effect is clear: access to reliable internet is becoming less tied to geography, unlocking new opportunities in education, logistics, agriculture, and emergency response.
What to watch next
SpaceX shows no signs of slowing its Starlink launch cadence. Future missions are expected to continue expanding capacity while refining satellite capabilities and ground infrastructure.
Unanswered questions remain around long-term orbital management, regulatory oversight, and how global competitors will respond. But in the near term, the trajectory is unmistakable.
The Starlink 6-100 mission may be one launch among many, but it captures a broader truth about today’s space economy: execution at scale is now the decisive factor.
This article is based on publicly available reporting from Space.com and official SpaceX launch information. Some technical details may evolve as post-launch data is released.



![[CITYPNG.COM]White Google Play PlayStore Logo – 1500×1500](https://startupnews.fyi/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/CITYPNG.COMWhite-Google-Play-PlayStore-Logo-1500x1500-1-630x630.png)